Design of Port of Restricted Orifice Surge Tank (2021.11.28)
Introduction
In the hydraulic design of restricted orifice surge tank, the discharge coefficient of port is important parameter. For the short port structure, the discharge coefficient of port is usually set to nearly 0.9 and this value is almost true. However, the discharge coefficient of long port sometimes exceeds 1.0. Therefore, it is important for the proper hydraulic design of restricted orifice surge tank to estimate the discharge coefficient of the port by appropriate method. In this report, the estimation method of port resistance and discharge coefficient of a restricted orifice surge tank established by Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry (CRIEPI) is introduced.
Theorem
Required parameters for design
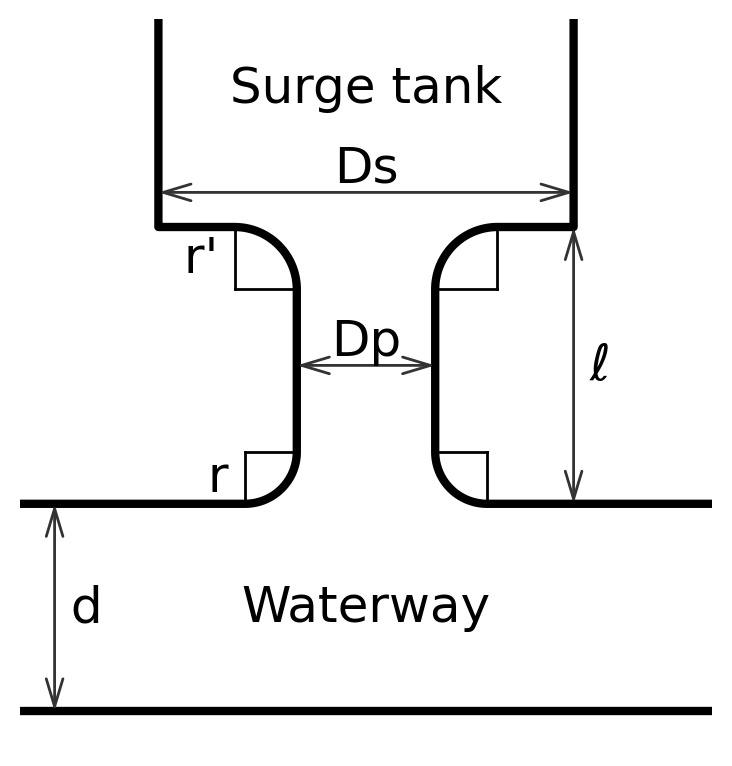
Head loss of port
The head loss of port of can be expressed as follow.
Interference factor
An interference factor for flow-in of and that for flow-out
can be defined using Figure-2depending on parameters of
and
.
Where,


Head loss due to right angle branch
The head loss due to right angle branch of can be estimated using following equations.
(a) Flow-in
(b) Flow-out
Where,
Using above,

Head loss due to section suddenly changed
The head loss due to section suddenly changed of can be estimated using following equations.
(a) Flow-in (sudden expansion)
(b) Flow-out (sudden reduction)
Where,
Using above,
Head loss due to friction
The head loss due to friction of can be estimated using following equations.
Summary of head loss calculation
From above, the head loss of port of can be expressed as follow.
Calculation of discharge coefficient
The port discharge can be expressed as follow using the port discharge coefficient of
and port resistance of
.
When Bernoulli's theorem is applied between waterway and surge shaft after interception referring Figure-4, following can be established.
Where,

Since during flow-in and
during flow-out, the port resistance of
can be expressed as follow.
Therefore,
From above, the port discharge of can be expressed as follow.
Procedure of calculation
Input parameters
Parameters for calculation
Calculation of port resistance
Interference factor
Define the interference factor for flow-in of and that for flow-out
from Figure-2 depending on the parameters of
and
.
Head loss coefficient due to right angle branch
Head loss coefficient due to section suddenly changed
Head loss coefficient due to friction
Summary of head loss coefficient
Port resistance
Calculation of discharge coefficient
Example of calculation
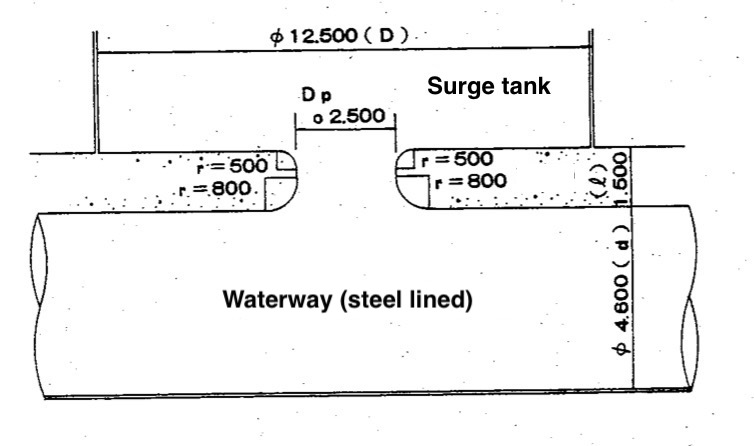
(1) Input parameters
| Roughness coefficient of port | | 0.013 |
| Shaft diameter | | 12.500 (m) |
| Port diameter | | 2.500 (m) |
| Waterway diameter | | 4.600 (m) |
| Port length | | 1.500 (m) |
| Radius of lower bevel | | 0.800 (m) |
| Radius of upper bevel | | 0.500 (m) |
| Maximum discharge | | 69.000 (m$^3$/s) |
| Gravity acceleration | | 9.8 (m/s$^2$) |
(2) Parameters for calculation
(3) Interference factor
From Figure-2, the interference factors can be defined as follows.
(4) Head loss coefficient due to right angle branch
(5) Head loss coefficient due to section sudden changed
(6) Head loss coefficient due to friction
(7) Summary of head loss coefficient
(8) Resistance of port
(9) Discharge coefficient of port
Program
Sample code
import numpy as np g=9.8 # gravity acceleration def inp_saku(): n=0.013 # Manning's roughness coefficient of port ds=12.5 # shaft diameter dp=2.5 # port diameter dd=4.6 # waterway diameter ell=1.5 # port length r1=0.8 # radius of lower part of port r2=0.5 # radius of upper part of port qq=69 # maximum discharge return n,ds,dp,dd,ell,r1,r2,qq def inp_bacai(): n=0.011 # Manning's roughness coefficient of port ds=12.5 # shaft diameter dp=3.0 # port diameter dd=5.5 # waterway diameter ell=26.6 # port length r1=0.5 # dradius of upper part of port r2=0.5 # radius of lower part of port qq=174 # maximum discharge return n,ds,dp,dd,ell,r1,r2,qq def main(): # (1) data input n,ds,dp,dd,ell,r1,r2,qq=inp_saku() #n,ds,dp,dd,ell,r1,r2,qq=inp_bacai() # (2) parameters psi=np.round((dp/ds)**2, decimals=3) phi=np.round((dp/dd)**2, decimals=3) delta=np.round(ell/dp, decimals=3) rho1=np.round(r1/dd, decimals=3) rho2=np.round(r2/ds, decimals=3) # (3) interference factor mu_i=1.230 mu_o=1.190 if 6.0 <= delta: mu_i=1.0 if 6.0 <= delta: mu_o=1.0 # (4) head loss coefficient due to section suddenly changed fse=np.round((1-psi)**2, decimals=3) fc=np.round(0.055/np.sqrt(0.003+rho2)*0.5*(1-1.144*psi)*(1+0.740*psi), decimals=3) # (5) head loss coefficient due to right angle branch cfb_i=np.round((phi**2-0.1*phi+0.4)*(1-0.9*np.sqrt(rho1/phi)), decimals=3) cfb_o=np.round(0.4*((1-2.5*np.sqrt(rho1))*phi**2+2), decimals=3) # (6) head loss due to friction df=np.round(delta*124.5*n**2/dp**(1/3), decimals=3) # (7) summary of head loss coefficient zeta_in=np.round(mu_i*(cfb_i+fse)+df, decimals=3) zeta_ot=np.round(mu_o*(cfb_o+fc)+df, decimals=3) # (8) head loss of port vp=np.round(4*qq/np.pi/dp**2, decimals=3) # velocity of port k_in=np.round((zeta_in-(phi**2-psi**2))*vp**2/2/g, decimals=3) # for flow-in k_ot=np.round((zeta_ot+(phi**2-psi**2))*vp**2/2/g, decimals=3) # for flow-out # (9) discharge coefficient of port cd_in=np.round(1/np.sqrt(zeta_in-(phi**2-psi**2)), decimals=3) # for flow-in cd_ot=np.round(1/np.sqrt(zeta_ot+(phi**2-psi**2)), decimals=3) # for flow-out # Print out of result print('# (1) Input parameters') print('Roughness coefficient n ={0:6.3f}'.format(n)) print('Shaft diameter ds ={0:6.3f} (m)'.format(ds)) print('Port diameter dp ={0:6.3f} (m)'.format(dp)) print('Waterway diameter dd ={0:6.3f} (m)'.format(dd)) print('Port length ell={0:6.3f} (m)'.format(ell)) print('Radius of lower bevel r1 ={0:6.3f} (m)'.format(r1)) print('Radius of upper bevel r2 ={0:6.3f} (m)'.format(r2)) print('Maximum discharge qq ={0:6.3f} (m3/s)'.format(qq)) print('# (2) Parameters for calculation') print('psi ={0:6.3f}'.format(psi)) print('phi ={0:6.3f}'.format(phi)) print('delta ={0:6.3f}'.format(delta)) print('rho1 (lower) ={0:6.3f}'.format(rho1)) print('rho2 (upper) ={0:6.3f}'.format(rho2)) print('# (3) Interference factor') print('mu_i ={0:6.3f}'.format(mu_i)) print('mu_o ={0:6.3f}'.format(mu_o)) print('# (4) Head loss coefficient due to section sudden changed') print('fse ={0:6.3f}'.format(fse)) print('fc ={0:6.3f}'.format(fc)) print('# (5) Head loss coefficient due to right angle branch') print('cfb_i ={0:6.3f}'.format(cfb_i)) print('cfb_o ={0:6.3f}'.format(cfb_o)) print('# (6) Head loss coefficient due to friction') print('df ={0:6.3f}'.format(df)) print('# (7) Summary of head loss coefficient') print('zeta_in={0:6.3f}'.format(zeta_in)) print('zeta_ot={0:6.3f}'.format(zeta_ot)) print('# (8) Resistance of port') print('vp ={0:6.3f} (m/s)'.format(vp)) print('k_in ={0:6.3f} (m)'.format(k_in)) print('k_ot ={0:6.3f} (m)'.format(k_ot)) print('# (9) Discharge coefficient of port') print('cd_in ={0:6.3f}'.format(cd_in)) print('cd_ot ={0:6.3f}'.format(cd_ot)) #--------------- # Execute #--------------- if __name__ == '__main__': main()
Example of output
# (1) Input parameters Roughness coefficient n = 0.013 Shaft diameter ds =12.500 (m) Port diameter dp = 2.500 (m) Waterway diameter dd = 4.600 (m) Port length ell= 1.500 (m) Radius of lower bevel r1 = 0.800 (m) Radius of upper bevel r2 = 0.500 (m) Maximum discharge qq =69.000 (m3/s) # (2) Parameters for calculation psi = 0.040 phi = 0.295 delta = 0.600 rho1 (lower) = 0.174 rho2 (upper) = 0.040 # (3) Interference factor mu_i = 1.230 mu_o = 1.190 # (4) Head loss coefficient due to section sudden changed fse = 0.922 fc = 0.130 # (5) Head loss coefficient due to right angle branch cfb_i = 0.141 cfb_o = 0.799 # (6) Head loss coefficient due to friction df = 0.009 # (7) Summary of head loss coefficient zeta_in= 1.316 zeta_ot= 1.115 # (8) Resistance of port vp =14.057 (m/s) k_in =12.406 (m) k_ot =12.102 (m) # (9) Discharge coefficient of port cd_in = 0.901 cd_ot = 0.913
Reference
- 技術研究報告 NO.65003 基本形ポートの水頭損失に関する実験的研究 1965.4 電力中央研究所技術研究所
- 奥清津第二発電所の調圧水槽のサージングおよび水撃圧の検討 藤野・橋本・芳賀 No.263 電力土木 1996.5
以 上